Warming Up to Cold Forming
August 14, 2014

New product development (NPD) teams are always looking for a competitive edge that will allow them to make their electronic devices smaller, appliances more reliable, vehicles safer, or instruments more precise. These products often call for highly engineered metal components on an increasingly miniaturized scale, and the demand for these miniature and micro metal components is accelerating. Those developing such products have a variety of choices in sourcing these components, seeking to meet critical functional specifications without compromise to design for manufacture (DFM), design for assembly (DFA), quality, and cost.
Weighing the available processes against one another according to cost-benefit criteria by which they are typically assessed brings to the forefront one process that is often overlooked.
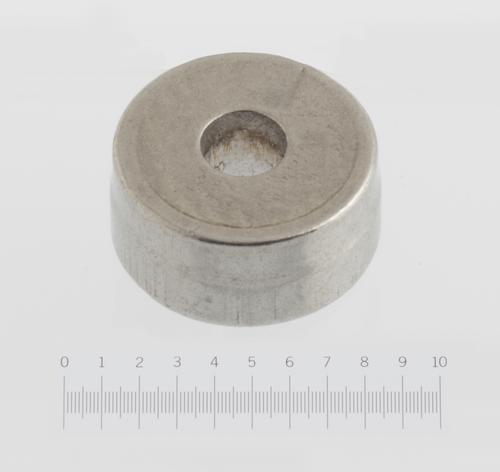
Cold forging, or cold forming, is the application of force with a punch to a metal blank staged in a die. The force exceeds the alloy's elastic limit, causing plastic flow until the metal blank assumes the shape bound by the punch and the die. As the name implies, this method of forming is achieved by force alone, forgoing the application of additional heat or cutting and shearing. Consequently, cold forming does not re-anneal or mechanically damage the material's original metallurgical grain structure like other processes can.
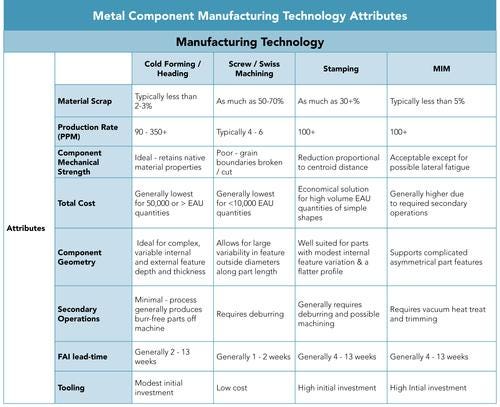
Consider the advantages and disadvantages highlighted in the table below. Following are three examples of cold forged components and a discussion of why it is that cold forming is so often overlooked when sourcing a component producer.
Glass to metal seal with terminal flattened and a pierced oval hole

Use: Terminal component in high volume glass to metal seal (hermetic) electronics devices
Material: Expansion Alloy: 52 alloy (nickel/iron alloy) per ASTM F-30 glass-to-metal seal quality
Manufacturing Method:
Formed and pierced on a slide machine, complete off machine
Notable Features:
Very good surface finish present on the sealing surfaces, no leak paths
Hole (oval) diameter is centered inside terminal flat area
Hole diameter held to plus or minus .002" ( plus or minus .05mm)
Flat end is trimmed perpendicular to lead axis
Advantages:
Material waste is minimal
Cold forming the pin eliminates the presence of spiral machining lines
Production speeds are high allowing for low production costs on high volume production runs, much faster than machining/much less material cost than machining
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





