Delo Adhesives Help the Auto Industry Keep It Together
A bevy of modern automotive components require crucial adhesives from Delo.
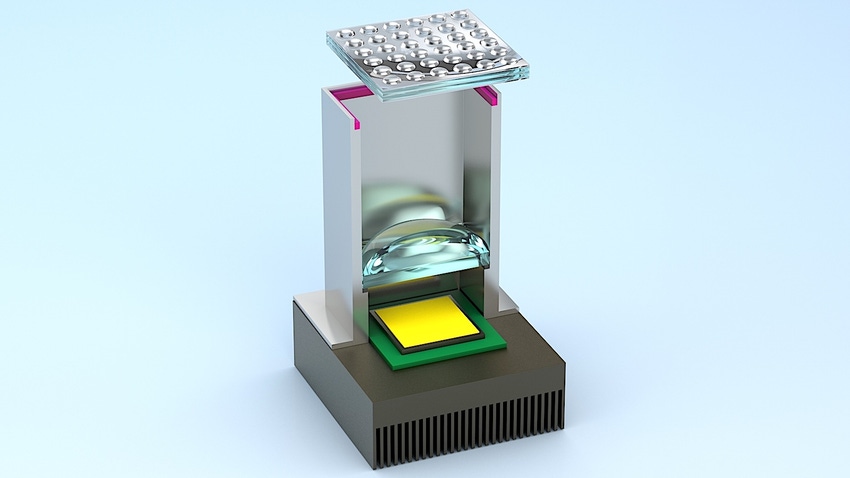
Bavarian commercial adhesives manufacturer Delo is successfully pressing its way into the automotive market with glues that are used in modern components such as electric vehicle battery packs and LED automotive lighting. Delo works with companies like Mercedes-Benz, Samsung, Bosch, and Foxconn in the auto industry.
Bosch uses the company’s Delo-Duopox TC8686 structural adhesive to glue 48-volt battery packs together for mild-hybrid vehicles.
An ordinary adhesive might work fine holding a battery pack together, but it could also insulate the battery cells from the housing, trapping heat inside the battery. Delo’s adhesive has a thermal conductivity of 1.0 W/(m·K), so it transfers battery cell heat to the housing, where it can be dissipated.
This lets Bosch simplify the production of its batteries by combining structural bonding and thermal management system mounting in one step instead of having to manually fix battery cells and then use gap fillers for heat dissipation. A degree of flexibility compensates for the different thermal expansion behaviors of cell and housing material during operation.
Delo says that it developed this product specifically for Bosch with industry-standard UL 94 V-0 flame retardance and tolerance of the battery’s wide temperature range of –40 °C to +180 °C. The company cites the adhesive’s tensile shear strength, which on aluminum is 18 N/mm². By optimizing it for manufacturing processes with good visibility to cameras, the adhesive is easy to for automated systems to detect. This lets Bosch apply the adhesive precisely for high quality assurance.
In LED automotive lighting, Delo has developed Photobond OB4189 to be resistant to yellowing, as shown by life cycle simulations of 500 hours at 140 °C. The modified acrylate is solvent-free and developed for a temperature application range of -40 °C to +120 °C. It has a compressive shear strength of 30 MPa on polycarbonate and 25 MPa on PMMA.
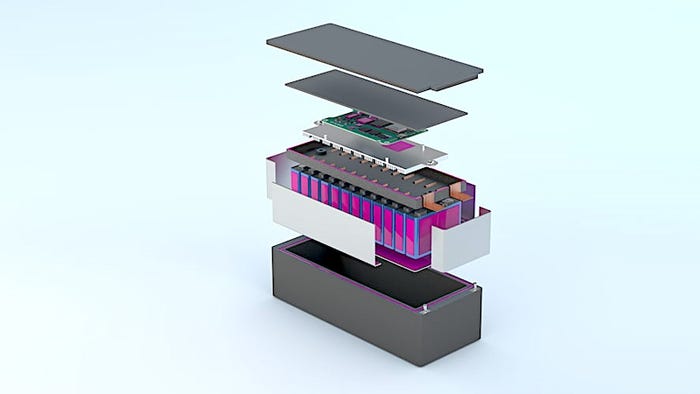
How the battery module's components are bonded together. DELO
It can be cured with UV light (365 nm) and visible light (400 nm). The typical exposure time at 400 nm with a layer thickness of 100 μm is 5 seconds. This enables high-precision active alignment processes for optical components and low cycle times in automated production.
Because of its high aspect ratio, this adhesive is particularly suitable for bonding microlens arrays, such as those found in LED headlights and projection systems.
Microlenses are often made of optically pure adhesive polymers to create microlens arrays fixed to a housing. Delo says that the adhesive retains its shape after dispensing and does not flow, which is important for bonding microlens arrays.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


