Beyond Lightweighting – 3DP in Aerospace
While lighter parts were the primary goal of additive manufacturing a few years ago, these days aerospace companies are looking for more from the technology.
January 13, 2022
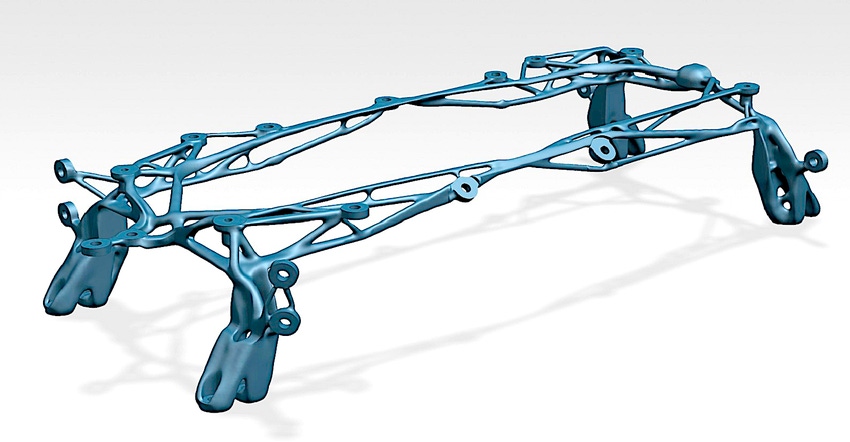
Additive manufacturing has taken a far more significant role in aerospace than it had 10 years ago. Now, the additive manufacturing process is used to build entire assemblies rather than replicating existing parts with lighter materials. Additive manufacturing is also able to create parts that are simply not possible with traditional casting or machining.
We caught up with Ivan Madera, CEO and founder of Nikon-backed Morf3D, to discuss the trends he is seeing in the aerospace additive manufacturing sector moving into 2022.
Design News: Is lightweighting still a major reason for using additive manufacturing in aerospace?
Ivan Madera: The initial thrust of additive manufacturing in aerospace was lightweighting. Now we’re creating optimized structures with freedom of design. That’s enablement. Through this technology, you can enable lightweighting and multi-functional structures. It’s lightweight, but it’s also a heat exchanger or an RF antenna. It has multidisciplinary use. That’s design freedom.
DN: What are some of the emerging benefits of additive manufacturing for aerospace?
Ivan Madera: The propulsion systems that rocket us to the Moon and Mars have a lot of 3D printed assemblies. If you look at the internal design of the parts, there is no way you could have created it through casting or machining. You can get more out of an additive manufactured object because you’re adding more complexity. That opens the possibilities for faster designs and faster launches.
This video from Electro Optical Systems – a partner of Morf3D – explains some of the areas of additive manufacturing this is getting widely used in aerospace.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like


.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)


