Harnessing the Power of Deterministic Networks for Motion Control
Motion control is propelled forward by cutting-edge network technologies, and conversely, network technologies are transformed to cater to the complex demands of equipment and processes. The almost symbiotic relationship between motion control applications and network technologies is shaping the way we design, run, and optimize machines as well as entire production lines.
In applications demanding precise and reliable data transfer, such as motion control, achieving synchronization and efficiency is paramount. For this purpose, deterministic operation and optimized network performance are essential components of motion control systems, especially when dealing with short cycle times. Even more, deterministic network technologies play a crucial role in enhancing various aspects of motion control, enabling the creation of ever-more ambitious setups.
Firstly, they contribute to accuracy and robustness by minimizing the impact of noise and any other signal transmission uncertainties that often plague such systems. By reducing these disruptive factors, deterministic networks help to maximize performance while improving the reliability of motion control processes. This is particularly beneficial in applications where even minor deviations can lead to significant discrepancies.
Secondly, the repeatability of motion control processes is enhanced through deterministic networks, as these ensure that the same results are achieved consistently with each transmission of a message across the network. Ultimately, this helps maintain a predictable and stable motion control operation while maximizing uptime.
Deterministic Networks Offer Future-Oriented Solutions
Until recently, standard Ethernet lacked inherent deterministic capabilities. As a result, to achieve this within industrial automation, network and automation experts followed two different routes. Some have been isolating networks to reduce the traffic load as well as protect time-critical messages from less transient, unpredictable traffic. Alternatively, deterministic performance was ensured by opting for network technologies offering it through specific protocols and topologies.
The introduction of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) IEEE 802.1 standards has brought a paradigm shift to standard industrial Ethernet, equipping it with deterministic capabilities and eliminating the need for non-standardized workarounds. This has significant implications for motion control applications, as network technologies with TSN functions offer distinct advantages.
For example, it is possible to achieve faster cycle times, supporting quicker operations without compromising on quality. In essence, the speed of production processes and efficiency that such systems are carried out with can be increased. Even more, TSN-driven components can enable the integration of a higher number of axes within motion control systems. This capability is particularly relevant for machine developers and users who seek to create more advanced setups with exacting quality requirements.
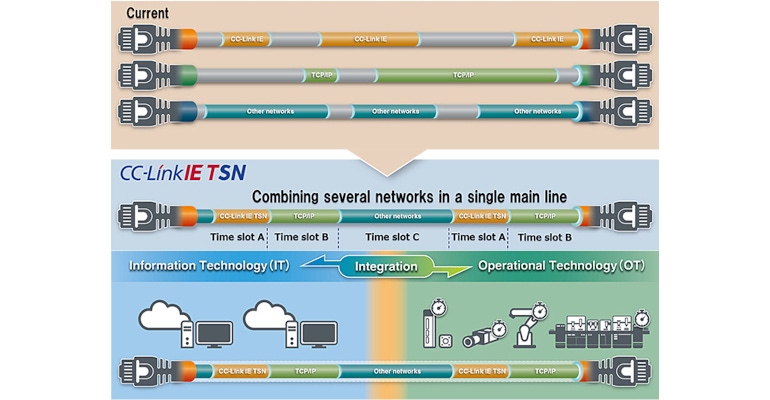
In addition to the technical benefits, the adoption of network technologies with TSN functions has broader implications for businesses. These solutions can play a pivotal role in enabling the digital transformation of industry. By accommodating both deterministic traffic, such as motion control data, and general-purpose TCP/IP messages, it is possible to create a converged network environment. This fosters the coexistence of various data streams, enabling businesses to harness data-driven insights for enhanced flexibility and responsiveness.
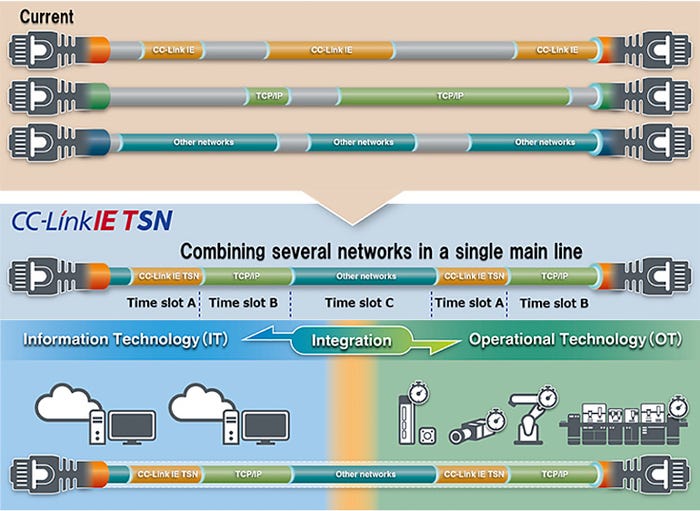
The deterministic network capabilities of CC-Link IE TSN means automation and control networks are not overwhelmed by network traffic, congestion, or competing Ethernet solutions. These precise network communications means that the complex timing required for sophisticated motion control and other automation uses are much more accurate.
Adopting TSN Now
Today, we are seeing the adoption of TSN-based automation solutions across a variety of sectors, with the first technology combining gigabit Ethernet and key IEEE 802.1 TSN standards for industrial applications. TSN has already been adopted by key automation vendors and machine builders, helping to ensure that the solutions they offer can effectively futureproof factory operations, particularly when developing advanced motion control systems.
Companies leveraging TSN are reporting key benefits, such as the ability to run a vast number of axes in sync. In effect, the solution can handle up to 256 nodes with accuracies in the order of ±1µs. In addition, forward-looking applications are converging information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) traffic within the same TSN network to support the realization of value-adding digital manufacturing strategies.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





