Case Study: Digital Radiography Adopts Lithium Polymer Batteries
October 10, 2011
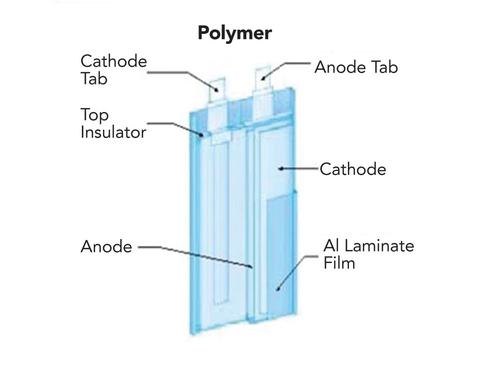
New digital radiography detectors are using lithium polymer batteries for power, making them one of the first medical devices to adopt the technology universally.
Modern digital radiography equipment uses conventional X-ray equipment and procedures to capture patient radiology images digitally on cassette-sized, wireless digital radiography detectors, which then transmit the images directly to the digital radiography system's capture consoles. Typical detectors are 14 inches by 17 inches and only half an inch thick. These small dimensions require exceptionally thin batteries. Many digital radiography detectors require the entire battery to be less than 5mm thick. That's the reason digital radiography detectors are adopting lithium polymer batteries.

Li-ion cells come in two basic form factors: cylindrical and flat lithium polymer cells. The most commonly used Li-ion cell is the cylindrical 18650 cell, used in most notebook computer applications. Several million 18650 cells are manufactured each month, and they offer the lowest cost per watt hour. The 18 refers to the cell diameter in millimeters, and 65-zero means that it's 65mm long.
Lithium polymer cells, sometimes called laminate cells, are available in custom footprint sizes. They can be very thin or quite large, depending on their intended use. The primary advantage of lithium polymer batteries is the variety of form factors available. With respect to cell construction, lithium polymer cells can either be rolled or stacked like a deck of cards. They are packaged in a flexible "coffee bag" material. The positive and negative terminals on the polymer cell are tabs protruding from the cell.
Lithium polymer batteries can be made very thin, down to around half a millimeter. However, much of the space is wasted by the packaging at the bottom of this range, so cells typically range from 2mm to 6mm thick. Many digital radiography detectors utilize cells just a few millimeters thick.
The length and width can also be quite large. Cell capacities can range anywhere from 50mAh for a small cell, such as one for a Bluetooth headset, to 10Ah or more for an electric vehicle battery. Typical cells used by digital radiography detectors support 2A to 3A hours.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





