3 Benefits VR and AR Offer Manufacturers Now
While applications are still emerging, VR, AR, and MR are already offering three key benefits for the manufacturers that are savvy enough to embrace them.
December 5, 2018
The manufacturing sector is facing a widening skills gap, even as more businesses are adopting Industry 4.0 technologies and processes. As the manufacturing industry continues to figure out the optimal combination of human worker and machine for various tasks, there’s no doubt that augmented, virtual, and mixed reality will become a vital interface for workers.
These technologies will become more commonplace in all factories as companies look to address the challenges of creating a workforce to meet the needs of digital manufacturing. But the exact applications are still yet to be determined. Although applications for these technologies are evolving, it’s already clear that there are three key benefits to embracing these visualization solutions:
1.) A Better Trained Workforce
Virtual and mixed reality can standardize training programs and make the overall process more effective. In a test conducted by Google’s Daydream team, which is responsible for the development of its virtual reality (VR) platform, researchers were able to show that VR training was more impactful than video training.
Two groups were trained on how to make an espresso. The VR team, which was able to virtually work an espresso machine and was guided through each step, was able to obtain a passing result after going through the physical task twice. The group that relied on YouTube videos to learn the steps for creating an espresso needed to attempt the physical task three times on average to reach a passing result. This is a small example of how interactive learning can expedite the training process in an industry like manufacturing.
|
A scene of Google's virtual espresso training program. (Source: Google Daydream) |
Using AR and VR for training helps to standardize the delivery of information. After all, person-to-person instruction can vary, depending upon the teacher—no matter their proficiency. Using visualization technologies ensures a uniformity of presentation of company-approved training programs, with progress and results for each participant being logged automatically.
Necessary safety orientation and skills development can take place offline, without impacting current production or putting inexperienced workers at risk. Novice technicians can use augmented reality (AR) to collaborate with more experienced workers, but this can also be beneficial to veteran employees.
Because intelligent manufacturing places a premium on constant improvement, refresher courses and advanced training—coupled with AR and VR—make it easier to administer tests, track progress, and issue certifications even through a widely dispersed workforce. As the industry places an increased focus on recruiting skilled workers, streamlining and developing effective training courses that optimize AR/VR technologies will only increase in importance.
RELATED ARTICLES:
2.) Simplified Maintenance Operations
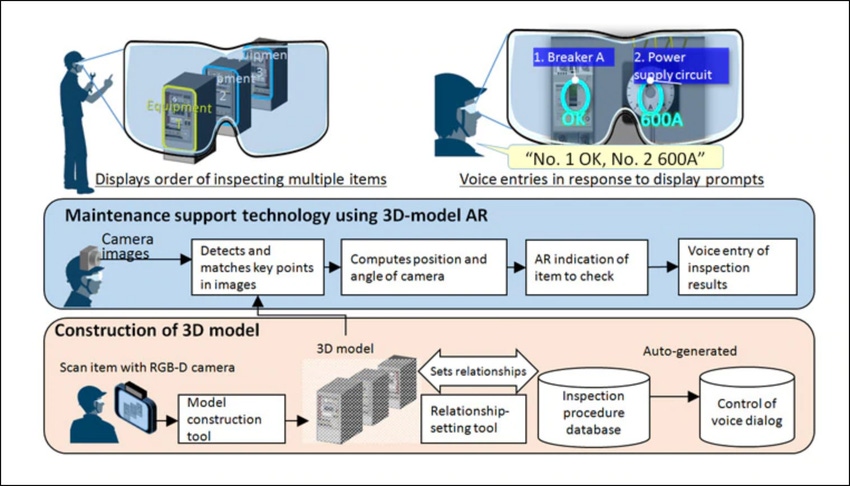
Augmented reality is not only invaluable as a teaching tool, but can also be used to guide technicians through complex, repetitive tasks that must be done right every time. One example of this comes from Mitsubishi Electric, which has developed an inspection and maintenance system that utilizes 3D AR smart glasses. Mitsubishi's technology first makes a 3D model of a machine with a tablet camera. The 3D scan interacts with the glasses to provide a visual checklist that guides the technician through which components of the machine should be inspected. The technician can even verbally fill out an inspection report as he or she is completing each step.
|
Mitsubishi Electric leveraged AR to create a platform for inspection and testing. (Image source: Mitsubishi Electric) |
While visualization through smart glasses helps to improve productivity, there is even more potential in the area of equipment maintenance and repair. Many companies are working on solutions that let you “see through machines” so that technicians can know the exact locations of components that would otherwise be hidden to the naked eye. Eventually, displays will show the real-time performance of machinery based on various sensors incorporated throughout the facility—no matter where it may be located.
3.) Improved Quality Assurance
While improved training and equipment maintenance will enhance productivity and reduce downtime, quality assurance can also benefit from advancements in VR and AR. As with the above examples, interactive AR glasses can provide step-by-step instructions on how to properly inspect various objects: what common flaws to look for, what testing equipment to utilize, and more. However, the technology has the potential to go beyond this and enter the realm of optical digitalization. 3D scanning for quality assurance is already a critical tool for many industries. It’s used to compare a final part to its original CAD design and ensure that all specifications are being properly met. Before long, it will be common for this scanning and analysis to be conducted at every stage of production via the employees’ headset or glasses.
David Hunter is the CEO of Star Rapid, a provider of prototyping, rapid tooling and low-volume manufacturing services.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like



.jpg?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

