Sustainability and Smart Tech Will Revamp Manufacturing in 2024
Two major trends that will drive manufacturing in 2024 include improved sustainability and the greater adoption of smart technology.
December 27, 2023
At a Glance
- Sustainability in manufacturing
- Increased traceability
- Coping with government regulations
According to industry experts, 2024 will see manufacturers spend more time and resources on sustainability. They are also likely to accelerate the adoption of smart technology, from AI to traceability tools. Partnerships and collaboration will also be a factor in the growing move to smart technology.
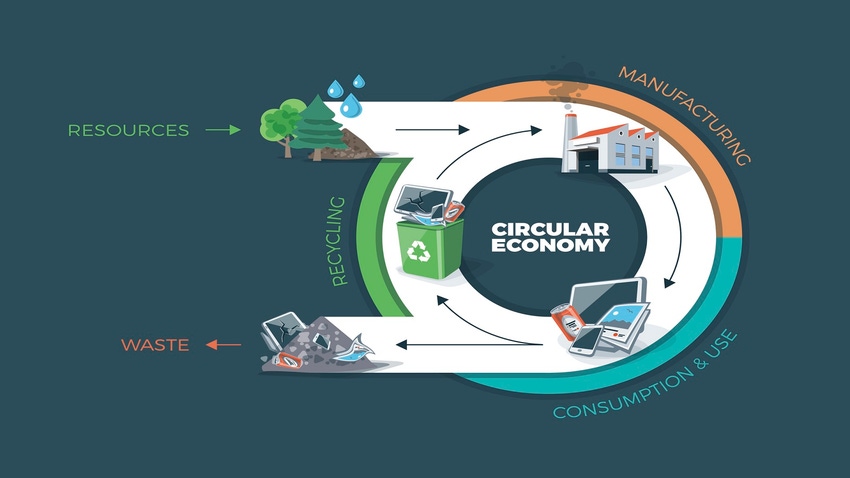
Sustainability regulations are expected to increase in the coming year. That will prompt manufacturers to think carefully about their production processes. “While sustainability is one of those things that's long been in the background, in 2024 it’s going to take a more front and center position, especially in the European Union, as more regulations are introduced around emissions standards and carbon footprints,” Henrik Hulgaard, VP of product management at Configit told Design News. “Once the digital product passport goes into effect in the EU, this will require companies to be able to show consumers information such as data on raw material extraction, production, and recycling.”
As with many EU regulations, they will come with consequences. “There will be more teeth to these regulations than ever before, incentivizing organizations to set goals and meet those goals – and disclose this information in their reports,” said Hulgaard. “Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues are becoming a bigger imperative around the world and more organizations will need to be able to show in their financial statements their progress in meeting benchmarks.”
As well as making progress on ESG issues, manufacturers will also have to show the progress to stakeholders. “To be able to have all of this information readily accessible to consumers – and stay competitive as customers increasingly prioritize sustainability in their purchase decision-making processes – manufacturers will need to more closely inspect their internal processes around transparency as well as looking at their carbon footprint and emissions,” said Hulgaard.
Government Pressure Will Drive Sustainability
A wide range of governmental moves will increase the importance of environmental concerns at manufacturers. “With the growing visibility of climate change impacts, manufacturers worldwide are placing a heightened emphasis on sustainability. Across industries and governments globally, there is widespread adoption of objectives to achieve carbon neutrality,” Doug Lawson, CEO of ThinkIQ told Design News. “The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has already put forth a proposal, urging companies to disclose their greenhouse gas emissions to investors, aiming to enhance ESG transparency and diminish their carbon footprint. The SEC’s proposal, coupled with the Paris Agreement’s call for a net zero economy by 2050, are forcing manufacturers to find ways to cut emissions and increase sustainability initiatives.”
To cope with these greater pressures, manufacturers are likely to increase the use of advanced technology. “We expect smart manufacturing technologies to play a crucial role in the new year to drive sustainability efforts in manufacturing,” said Lawson. “Supply chain traceability solutions can capture, contextualize, and analyze data related to energy consumption, carbon emissions, and waste. This will provide manufacturers with the insights they need to identify opportunities for reducing their environmental impact.”
A Surge in Global Partnerships to Accelerate Smart Manufacturing
Manufacturers are likely to also use smart tech tools to expand production and market reach. “The globalization of smart manufacturing has been shaped by technological advancements, enabling businesses to expand their operations on an international scale. Consequently, an increased number of organizations are broadening their reach across global boundaries,” said Doug Lawson of ThinkIQ. “In 2024, we expect a substantial surge in global partnerships, aiming to expedite the integration of smart manufacturing practices. Organizations will collaborate more with external partners, including startups, research institutions, and third-party communities, within open innovation ecosystems.”
As an example, Lawson points to CESMII, Confinity-X, Catena-X, and International-X for their various initiatives aiming to accelerate the global adoption of smart manufacturing. “This collaborative approach facilitates the exchange of ideas, expertise, and resources, leading to accelerated innovation and the development of cutting-edge solutions worldwide,” said Lawson. “As business leaders continue to harness advanced technologies and embrace global interconnectivity, they are positioned to unlock unprecedented levels of innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness in the year ahead.”
Manufacturers Will Use Artificial Intelligence to Combat Inflation
Inflation is another challenge for manufacturers. AI will likely play a role in helping to manage inflation pressures. “With inflation wreaking havoc up and down the entire supply chain, manufacturing companies are looking for ways to stabilize their operations and increase efficiency,” said Lawson. “The constant increase in prices of raw materials has forced manufacturers to look for ways to improve efficiency and productivity, at reduced costs, with a dependable output of high-quality products. Artificial Intelligence is opening up greater possibilities for more optimized manufacturing processes to these ends.”
Lawson noted that over the next year, we can expect inflation to drive more and more manufacturers to look to AI to successfully navigate the challenges posed by a higher cost in materials.
Discrete Manufacturers Will Adopt Industry 4.0 Solutions
Discrete manufacturers in particular will likely turn to smart technology to improve operations. “The discrete manufacturing landscape continues to face enormous headwinds, putting stress on every aspect of business, including the global supply network. Adding to that are new sustainability requirements, and significant worker retention issues,” said Lawson. “Discrete manufacturers are being forced to re-examine every aspect of their business, paving the way for a more resilient and collaborative approach to address these challenges. The post-pandemic move toward supply chain regionalization is also adding stress to an already heavily burdened manufacturing workforce.”
Lawson expects we will see more and more discrete manufacturers rethinking the way they use data to empower people and inform strategies, both for real-time operations and on a longer horizon for resource planning and predictions.
Traceability Will Gain Traction in 2024.
Finally, increased use of advanced traceability will play a role in improving manufacturing operations. “In the EU, the forthcoming digital product passport regulations are expected to start rolling out in 2026,” said Henrik Hulgaard of Configit. “These will require companies to be able to show what is essentially a digital record of a product’s sustainability and circularity information throughout its lifecycle, from design to end-of-life,”
Hulgaard noted that regulations like this, coupled with the increased adoption of technologies like digital twins, will drive the need for traceability in terms of being able to see how a product is designed, manufactured, sold, and serviced. “Organizations will need to look more closely at how to create comprehensive visibility across functions to meet this need,” said Hulgaard.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





