Manufacturers Gain a Competitive Edge by Using Tech in the Workforce
Manufacturers can use technology to improve the work environment and enhance individual skill sets, bolstering a competitive edge.
August 7, 2023

Gerry Abbey, analyst relations manager at Rockwell Automation
As the saying suggests, a team's strength relies on its weakest link, and in the highly competitive manufacturing sector, manufacturers who attract, retain, and enhance the skills of the right team will outperform competitors. However, Rockwell Automation’s 8th Annual State of Smart Manufacturing report sheds light on the concerns of over 1,350 manufacturers worldwide, revealing that a skilled workforce remains a top concern.
The 2022 report indicated that 35% of respondents believed they would be unable to outpace the competition due to the lack of a skilled workforce. In the 2023 report that figure rose to 46%, making it the primary reason manufacturers endeavor to navigate an increasingly complex landscape and address multiple workforce issues simultaneously.
Workforce Challenges Require Modern Solutions
Modern solutions are required to tackle unique challenges such as a shortage of skilled workers, worker retention, and upskilling. According to the State of Smart Manufacturing Report, respondents identified effective management of people and resources as the most notable leadership challenge for manufacturers over the next 12 months. Additionally, understanding how to manage next-generation workers ranked third on the list of leadership obstacles.
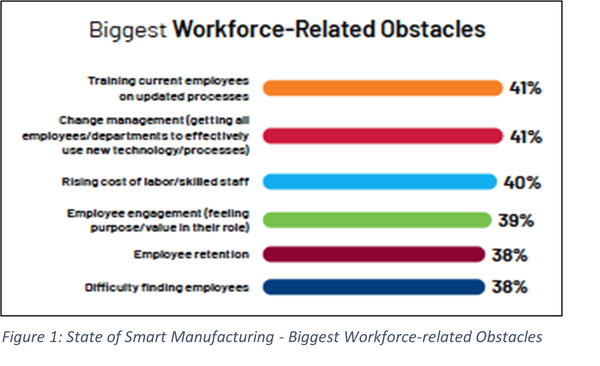
When examining the biggest obstacles related to the workforce (as depicted in Figure 1), training current employees on updated processes emerged as the primary challenge, tied with change management, an often unappreciated yet essential component for successful technology adoption. This was followed by the rising cost of labor and skilled staff, employee engagement, retention, and the difficulty of finding employees. Notably, the percentage distribution across all six responses was merely 3%, indicating that manufacturers prioritize these obstacles closely. More than two-thirds of manufacturers believe that technology can help address these workforce challenges.
While most participants intend to use smart manufacturing technology this year, success cannot be achieved by technology alone, nor can it be achieved solely through people. To see meaningful success gained from technology, equal emphasis must be placed on hiring and training the appropriate workforce. Leaders among our respondents show a clear understanding of this importance and are growing their workforce as a result, with 31% expecting to increase their headcount this year.
Technology Advances Manufacturing Operations
Digital transformation is driving a significant shift in manufacturing operations. Organizations are leveraging advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), cloud computing and automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency and enhance customer experiences. When adopting these technologies, it is crucial not to overlook the human element. Strengthening the connection between technology and people is more critical than ever, with an eye toward the future.
Across the manufacturing ecosystem, manufacturers are actively seeking a skilled workforce to fortify the tech-human connection, gain enterprise-wide advantages and sustain these technologies to meet both short- and long-term goals. Manufacturers can utilize technology in various ways to attract, retain, and enhance the skills of the workforce, thereby sharpening their competitive edge.
The implementation of robotics and the automation of repetitive and mundane tasks allow the manufacturing workforce to concentrate on more complex and value-added activities. This not only enhances efficiency but also boosts job satisfaction as employees engage in more interesting work, providing opportunities for learning and developing new skills in operating, optimizing, and maintaining automated tools and systems.
Digital Recruitment and Opportunities for Growth
Even before employees join a manufacturing organization, technology can facilitate a positive experience. Digital platforms and recruitment tools such as online job portals and video interviews can broaden the reach of recruitment efforts and streamline the hiring process, making it more efficient and appealing to potential candidates.
Employee turnover poses challenges for all industries and the loss of knowledge and associated costs with recruitment and training are undesirable. While implementing the latest technology can help attract the next generation of workers, manufacturers must also foster a culture that encourages employee retention—especially as Baby Boomers and Generation Xers retire, taking their industry knowledge with them. Technological advancements give rise to new job roles and transform existing ones. For instance, the digitized manufacturing ecosystem revolves around data, leading to high demand for data scientists, AI engineers, cybersecurity experts, and software architects.
By utilizing technology platforms to assess the skills of current and prospective employees, manufacturers can identify skill gaps. For existing workers, targeted skills development training programs can be offered, enabling them to learn about data management, the operation of new tools and technologies, and optimization practices. This expands their knowledge base and skill set. Engaging workers in training and upskilling activities through gamification technologies and microlearning platforms make learning interactive, enjoyable, flexible, and easily accessible. This promotes continuous learning and skills development. Furthermore, hiring new staff with expertise in technology areas enhances manufacturers' ability to fully leverage the potential of emerging technologies.
Flexible Work, Employee Support, and Collaboration
Technology empowers manufacturers to offer remote work options, expanding their access to a broader talent pool. While manufacturing has traditionally been site-based, remote management and monitoring of increasingly automated systems provide greater flexibility. By providing flexible work arrangements like remote work or flexible scheduling, manufacturers can attract workers who prioritize work-life balance, leading to improved retention rates.
Utilizing data analytics, ML algorithms, and predictive analytics, organizations can pinpoint areas where team members may require support and deliver targeted training to enable developmental growth.
Fostering an open and collaborative environment with team members encourages growth, builds mutual trust, and empowers employees to seize opportunities for development within the organization.
Collaborative technologies, such as project management software, communication platforms, and video conferencing tools, facilitate effective communication and teamwork, particularly for geographically dispersed teams. These tools improve productivity and enhance employee satisfaction by enabling seamless collaboration and communication.
While technological expertise is desirable, the 2023 State of Smart Manufacturing Report also uncovered manufacturers' desire for employees who can adapt to changing requirements and collaborate effectively in teams. Surprisingly, knowledge of smart technology ranked sixth among a range of "soft skills" identified in the report:
Communication/Teamwork
Flexibility/Adaptability
Employee Engagement
Employee Initiative
Analytical Thinking
Knowledge of Smart Technology
In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, to stay ahead of the competition, manufacturers that are progressive and effectively adopt and leverage new technologies gain a competitive advantage by improving productivity, enhancing customer experiences, and fostering innovation. Using technology to identify evolving job roles, bridge skills gaps, and recruit, retain, and upskill the workforce is vital to business continuity.
Manufacturers can leverage technology to create a more attractive work environment, and enhance individual knowledge bases, skillsets, and capabilities, which can improve employee retention and job satisfaction. Empowering staff with expertise in emerging technologies, alongside more traditional “soft skills” enables organizations to drive innovation, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and maintain their competitive edge.
You May Also Like



