Without the wireless connection, the IoT of everything would stop. Design News has the top 12 reasons why that is true.
June 25, 2020

The first wave of 5G-enabled devices dominated 2019, including the Galaxy S10, OnePlus 7, and Huawei P30 among others. Major infrastructure improvements continued to be rolled-out.
But 5G wasn’t the only new wireless tech hitting the market. Other wireless activities, like Wi-Fi 6, also began to appear. Below are 12 of the editor’s top picks for 2019.
|
Image source: Qualcomm |
Qualcomm has big plans for 5G in 2020
From photos to gaming and AI applications, the Snapdragon 765 and 865 are both focused on bringing 5G to consumers at all levels.
Qualcomm's latest Snapdragon platforms are aimed squarely at bringing 5G devices to consumers next year.
|
Image source: WiFi Alliance |
How Wi-Fi 6 and 5G will transform factory automation
A key technology trend for automation and control in 2020 and beyond is the emergence of wireless communications including 5G, Wi-Fi 6, LoRaWAN and more. An obvious benefit for factory automation is the use of wireless communication for remote monitoring and remote operation of physical assets but an equally important benefit is an ability to replace cables, unreliable WiFi and the many industrial standards in use today.
|
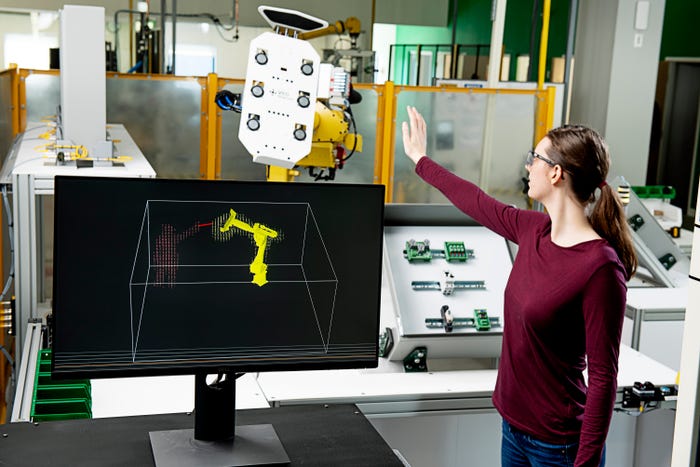
Image source: Veo Robotics |
FreeMove turns any industrial robot into a cobot
Veo Robotics' FreeMove platform gives standard industrial robots the ability to function as collaborative robots that work alongside human workers. Don't get rid of your old industrial robot yet. You may be able to upgrade it into a collaborative robot.
|
Image source: Beckstrom.com |
What are Beckstrom’s Laws of Cyber Security?
Prioritizing security efforts – critical for the IoT to survive – may best be done by considering the value of transactions over the size of the network.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has many defining characteristics, such as tiny, cheap and low power sensors, embedded computers, and connectivity. But one characteristic will rule them all, namely, security. In the very near future, the IoT will probably not exist if it isn’t secure.
|
Image source: Design News |
5G May Soon Explode with New Factory Functionality
Just as the iPhone ushered in a new world of consumer connectivity, the ultra-fast 5G networking may jump-start new industrial capabilities.
Speedy 5G networking is beginning to show up; in some places it is already a reality. While we know it will speed up consumer applications such as streaming or downloads – like a movie in seconds – what will it mean for industrial settings? At a session at the Design and Manufacturing Minneapolis show last week, Joshua Ness, senior manager of 5G Labs at Verizon, explained the coming impact of 5G during his session, Prepping for the 5G Factory.
|
Image source: NUS |
Smart' Textiles Boost Data Connectivity Between Sensors for Wearable Tech
A new textile network of sensors can provide the basis for intelligent wearable technology with unprecedented communication capability.
|
Image source: AiFi MWCLA, Design News |
AiFi Replaces Cashiers and Checkouts with AI
Walk in, get what you need, and walk out. AiFi uses AI to completely automate and streamline the shopping experience.
Imagine walking into a grocery store, picking up all the items you need, and walking right out the door. No need for a cashier or even a self-checkout, the store will automatically charge everything you take to your credit card.
|
Image source: WMG at the University of Warwick |
A European University is Testing 5G for Self-Driving Vehicles
The University of Warwick, in collaboration with NI, will be conducting tests of 5G-enabled services for autonomous and connected vehicles.
|
Image source: MOXA |
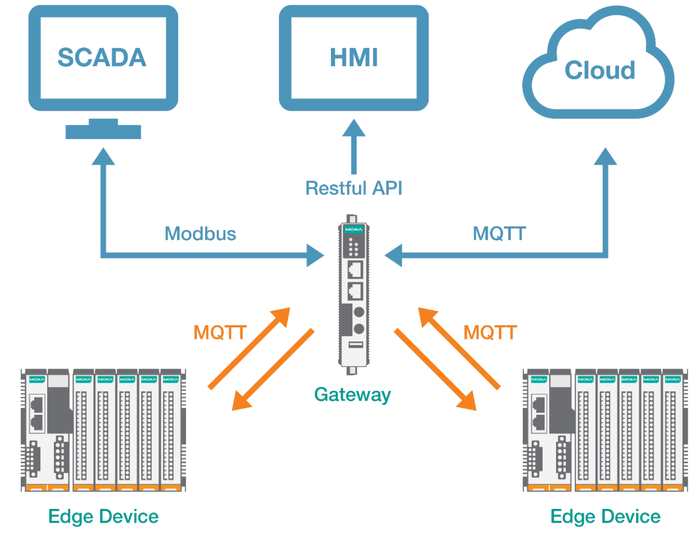
Edge Devices Leverage MQTT for IIoT Connectivity
The MQTT transport protocol has emerged as a top choice for implementing IoT connectivity, offering solutions using local gateways or direct to the cloud.
A primary challenge for IIoT automation and control applications is the ability to efficiently and effectively collect the data that becomes the grist for IoT enterprise-level, decision making and analytics. And while a wide variety and different types of edge devices have been introduced, a major concern is how to collect data from these devices.
|
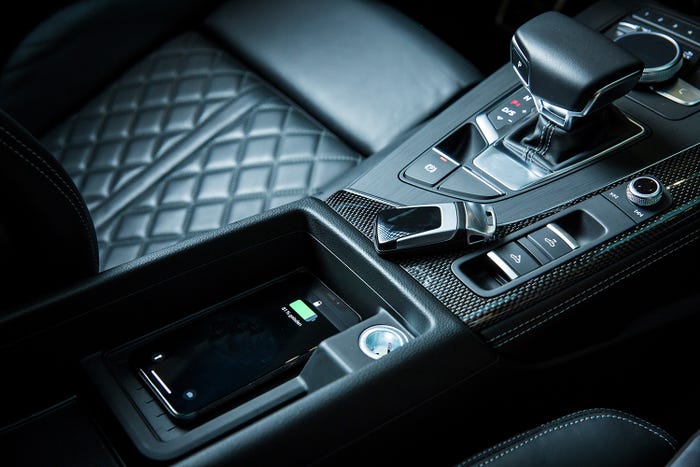
Image source: Molex |
The 4 Major Challenges of Wireless In-Vehicle Charging
Wireless charging is the best way for automakers to meet consumer demand for better charging performance in their vehicles. But there significant challenges to getting this innovation to market.
Today’s consumer expects to be connected via their mobile device wherever they go – especially in their vehicles, which have become more than transportation; they are a mobile extension of the owner’s living space.
|
Image source: LoRa Alliance |
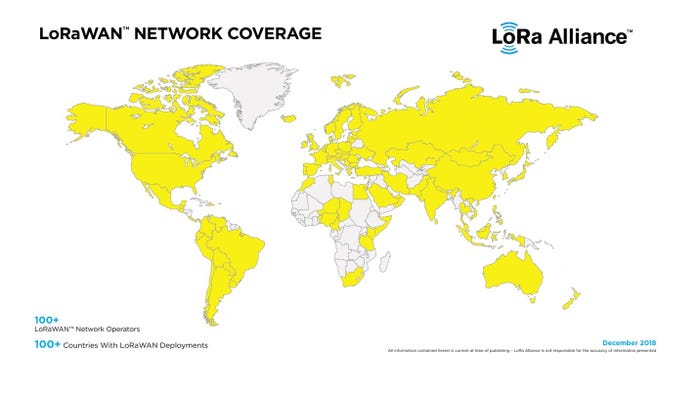
Everything You Need to Know about LoRa and the IoT
A guide to LoRa / LoRAWAN, the communications technology emerging as the leader among Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs) entering the IoT space.
We're entering a world in which WiFi and Bluetooth may no longer be the best communication technologies for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. The IoT is gaining more ground each year. Experts project there will be 75 billion connected devices by 2025.
|
Image Source: ODVA |
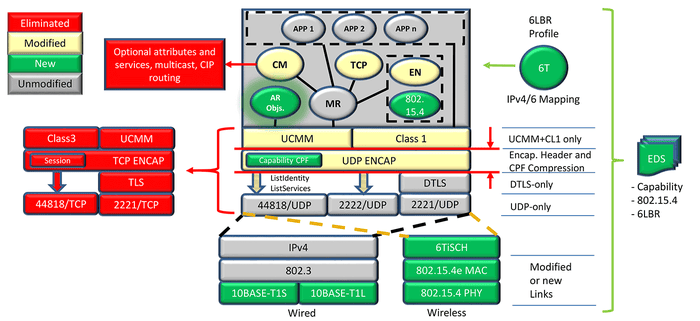
IoT-drive technology standards are creating new possibilities for reducing the cost and complexity of integrating Industrial Ethernet into constrained networks and devices.
John Blyler is a Design News senior editor, covering the electronics and advanced manufacturing spaces. With a BS in Engineering Physics and an MS in Electrical Engineering, he has years of hardware-software-network systems experience as an editor and engineer within the advanced manufacturing, IoT and semiconductor industries. John has co-authored books related to system engineering and electronics for IEEE, Wiley, and Elsevier.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like